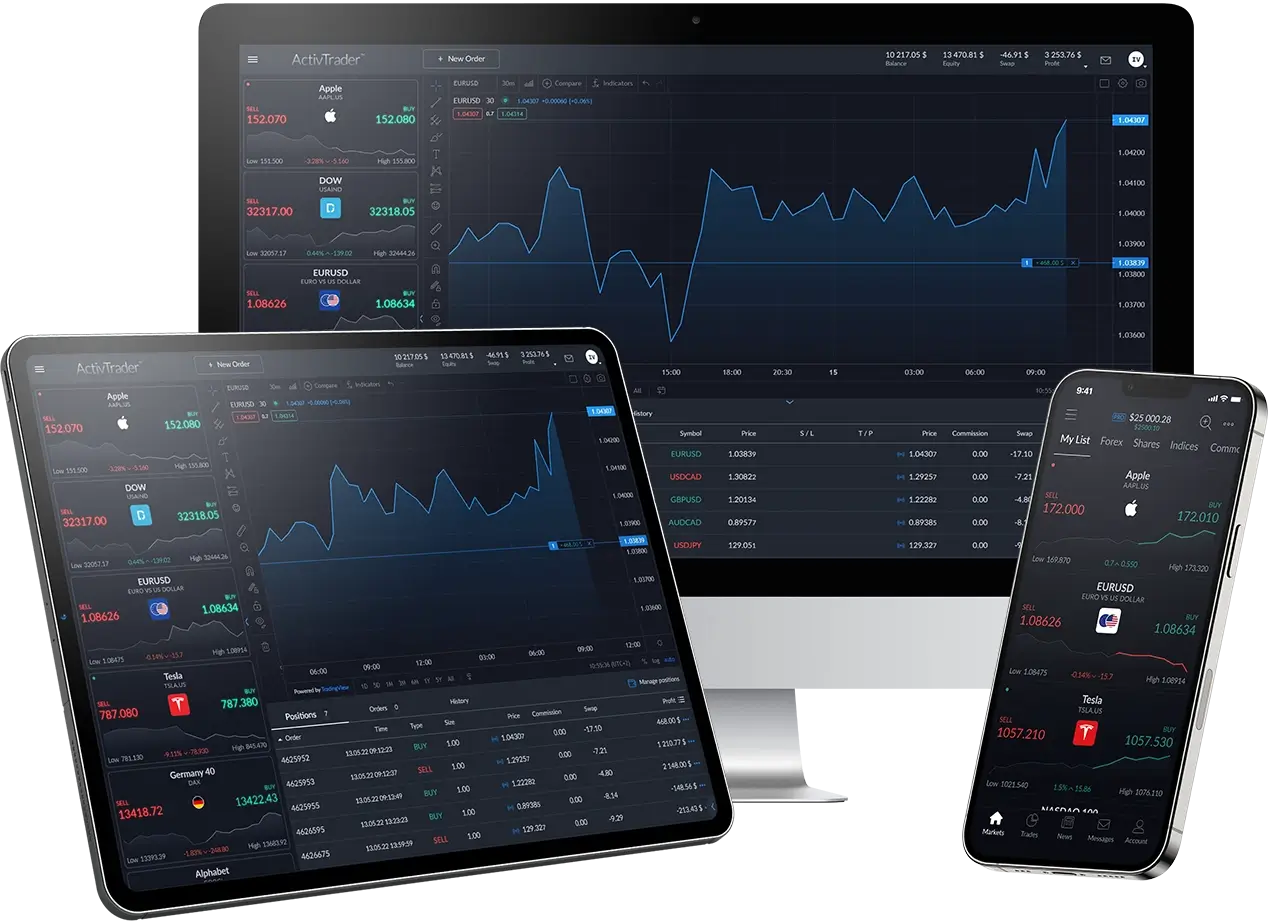
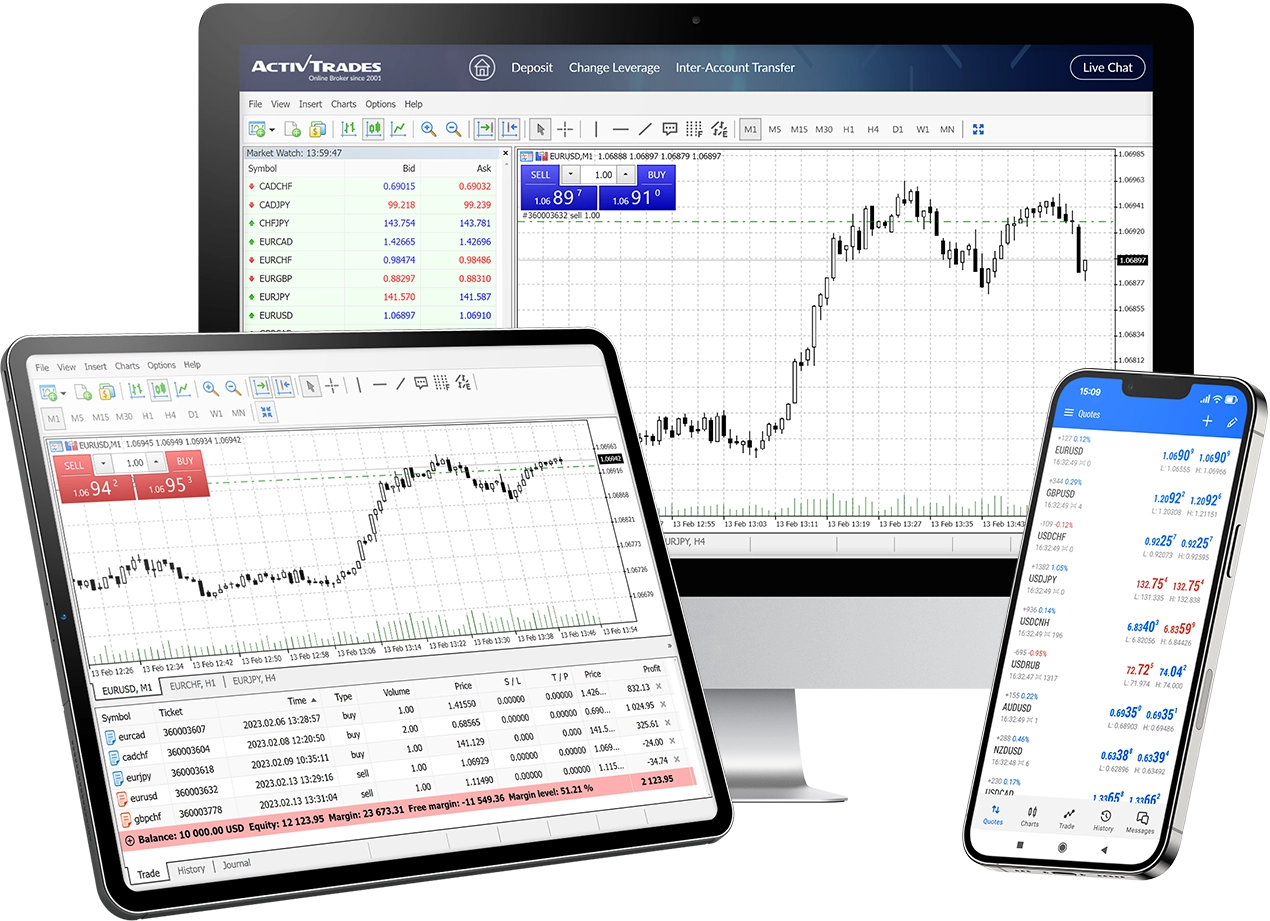
Shares Trading
Trade over 1000 CFDs on company shares from around the world with no stamp duty, custody or account management fees.
Invest With Any Capital
Trade fractional shares
Transparent Pricing
No mark-ups, no hidden fees
Go Long or Short
Receive dividend payments on long positions
Fund's Protection
Additional insurance to protect your capital
Award-Winning Support
Customer satisfaction rate over 95%
Best-in-class execution
Over 93.6% of orders filled at requested price or better
Why Trade Shares With Us

Transparent Pricing
Trade shares easily and affordably with no hidden fees or markups.

New Investor Profile
No Trading Fees with 1:1 Leverage
Choose the New Investor profile for zero commission and no swaps on shares, or trade leveraged shares with standard fees.

Corporate Actions
Dividends are paid on long positions, while the equivalent is charged on short positions.

Tobin Tax
CFDs on the Italian index and all Italian shares are subject to the Tobin Tax.
Diversify Your Portfolio
With 1000+ Instruments Across 7 Asset Classes
Frequently Asked Questions
Find quick answers to common questions about our services
Why are there big gaps in my price chart when viewing stocks?
Unlike FX, stocks don't trade around the clock during the working week. They usually trade throughout the business day of the region they're listed in. This is because there aren't usually markets in other countries offering the same stocks throughout the day as in the case of Forex (Asian/European/North American sessions).
This means that there are long periods in each day, and also over the weekend, where no trading activity is taking place. Now, even though the stock market may be closed, this doesn't mean there's no new information coming out that will change investors' beliefs or appetites for risk. These changes in outlook and sentiment are the main reasons for market gaps.
A market gap will occur when the stock reopens for trading and the market is struggling to price-in the developments that have taken place since the last time that market was live.
How do traders perform analysis on stocks? Is it different from FX analysis?
Broadly speaking, there are two main types of market analysis, technical and fundamental.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is simply the study of price action on the chart. Technical analysts do not concern themselves with geopolitical news, economic data, or anything else other than what the chart itself says.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis does differ between asset classes because you're dealing with the fundamentals of supply and demand, as well as the economic inputs and broader conditions that influence a specific asset's value. For FX this may be interest rates and other economic data, for crude oil it tends to be inventories and new wells. In the case of shares, traders pore over the financial statements of the companies they are trading, which those companies are obliged to provide.